CrewAI based Blog Writer using Local DeepSeek-R1 (vLLM)
CrewAI Blog Writer
[ Automating Blog Content Creation with Generative AI ]
CrewAI Overview
CrewAI is an advanced framework designed to optimize the orchestration of multiple AI agents for a wide variety of tasks, including automation, content generation, data extraction, and more. It allows the seamless coordination of independent agents, enabling them to collaborate and complete tasks that require different capabilities, such as data research, content writing, and specialized tasks like SEO optimization.
At the core of CrewAI’s functionality is its multi-agent architecture, where each agent is assigned specific roles or functions. These agents communicate and cooperate to execute workflows that involve complex tasks, making CrewAI particularly useful for tasks like content creation, marketing automation, research, and many other domains.
Key Features of CrewAI:
- Multi-Agent Orchestration: CrewAI enables agents to work together in a structured workflow, ensuring tasks are completed sequentially or concurrently depending on the need.
- Model Agnostic: CrewAI supports integration with various AI models, such as OpenAI, local models (e.g., DeepSeek), and any other models that may suit your specific needs. This flexibility makes it adaptable to various scenarios.
- Customizability: Each agent’s behavior and the overall workflow can be tailored to meet the unique requirements of the task. For example, agents can be designed to focus on different aspects of a project, like gathering information, writing drafts, or polishing content.
- Efficiency: By automating tasks such as research, writing, and editing, CrewAI reduces the time and effort needed to complete complex tasks, allowing for faster content generation and workflow execution.
CrewAI Architecture
Courtesy: https://docs.crewai.com/
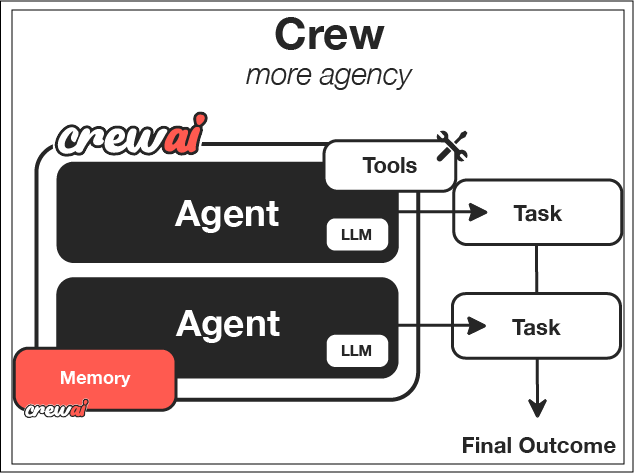
CrewAI based Blog Writer Implementation
The CrewAI Blog Writer leverages CrewAI's multi-agent framework to automate the entire blog creation process. By using specialized agents for each step of content creation—research, writing, and editing—the CrewAI Blog Writer ensures that the generated blog posts are not only high-quality but also SEO-friendly and well-researched.
Key Agents in CrewAI Blog Writer:
- Researcher Agent: The Researcher agent is responsible for gathering relevant information and insights about the blog topic. It mines trusted sources, such as websites, articles, and academic papers, to compile data that will inform the blog’s content. The Researcher agent ensures the generated blog post is backed by accurate and up-to-date information.
- Writer Agent: The Writer agent takes the insights provided by the Researcher and uses them to draft a structured, engaging, and coherent blog post. The Writer agent leverages language models, such as DeepSeek or other local LLMs, to generate text that is aligned with the user’s objectives, while maintaining clarity and flow throughout the article.
- Editor Agent: The Editor agent ensures the final draft is polished and optimized for search engines (SEO). It refines the content, checking for grammatical errors, enhancing readability, and ensuring that SEO best practices, such as keyword usage, meta tags, and content structure, are followed. The Editor agent may also optimize the blog post’s length and style, ensuring it meets the client’s requirements.
How It Works:
- Input: The user provides a blog topic, and the CrewAI Blog Writer system kicks off the workflow.
- Research Phase: The Researcher agent fetches relevant data and insights to inform the blog content. This may include checking industry news, analyzing competitors’ content, or mining data from authoritative sources.
- Writing Phase: The Writer agent uses the gathered insights to craft a high-quality, readable blog post. It focuses on creating a clear structure with sections, headings, and paragraphs that flow naturally.
- Editing Phase: The Editor agent refines the content by improving language, fixing errors, and ensuring the content is optimized for SEO. It ensures the blog post is both human-friendly and machine-friendly, improving its chances of ranking higher in search engine results.
Advantages of CrewAI Blog Writer:
- Automated and Efficient: The entire process of blog creation—from research to editing—is automated, saving considerable time and effort.
- Customizable Workflows: You can customize agents to suit your specific needs, for example, adjusting the Researcher agent to focus on a specific data source, or tailoring the Writer agent to follow a particular writing style.
- SEO Optimized Content: The final blog post is polished for SEO, ensuring better visibility and ranking in search engines.
- Model Flexibility: Since CrewAI is model-agnostic, it can work with various LLMs (like DeepSeek, OpenAI, or other local models), depending on the project requirements.
Technical Implementation
The CrewAI Blog Writer is built upon LangChain for model orchestration and CrewAI for managing the agents. Each agent is defined with its own role, task, and backstory, ensuring they perform their respective functions effectively. For example, the Researcher agent is set up with a specific goal of gathering insights from trusted sources, while the Writer agent focuses on drafting high-quality content.
This system is highly customizable, allowing you to adjust agent roles, tasks, and even integrate custom models or tools to further refine the blog creation process. The result is an efficient, scalable solution for automating the entire content creation process while maintaining high quality and relevance.
In summary, the CrewAI Blog Writer offers a comprehensive solution for businesses and individuals seeking to generate high-quality blog content efficiently and consistently. By automating the workflow and incorporating advanced language models, it ensures that every piece of content is thoroughly researched, expertly written, and optimized for SEO.
CrewAI based Blog Writer - Code Flow
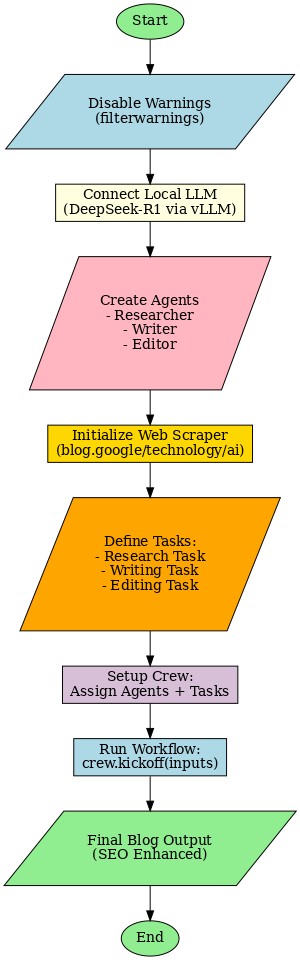
Pre-Requisites
1.Running Local LLM using vLLM
Before you can run the CrewAI Blog Writer locally with the DeepSeek-R1 model via the vLLM server, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- Python Environment: You need a Python 3.10+ environment. It is recommended to create a virtual environment for managing dependencies.
- vLLM Setup: The local LLM server should be set up using the vLLM framework. You can set it up by running the following command:
(vllm-env) (base) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/vllm-env$ python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8888 \
--device cuda \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.85 \
--max-model-len 32768 \
--max-num-seqs 1 \
--tensor-parallel-size 1 \
--swap-space 8
- GPU Support: Ensure you have a CUDA-compatible GPU with enough memory (at least 8GB VRAM) to run the DeepSeek-R1 model efficiently.
- vLLM Configuration: Ensure the vLLM server is configured correctly to run the model and serve the local API at http://localhost:8888/v1.
- Additional Dependencies: You will need the following Python packages:
- LangChain
- CrewAI
- crewai_tools
- Scraping tools (if using ScrapeWebsiteTool)
For detailed setup instructions, please refer to the full guide available at: vLLM Chatbot Setup Guide
2. Crew AI Installation
Follow these steps to install Crew AI and set up your environment for the CrewAI Blog Writer:
- Create Conda Environment: Begin by creating a new Conda environment for Crew AI.
(base) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/crewai$ conda create -n crewai_env python=3.11
(base) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/crewai$ conda activate crewai_env
(crewai_env) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/crewai$
- Install CrewAI: Install the core CrewAI package using pip.
(crewai_env) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/crewai$ pip install crewai
- Install CrewAI Tools: If you need the additional tools for scraping, optimization, etc., install the extended version with tools.
(crewai_env) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/crewai$ pip install 'crewai[tools]'
- Install LangChain Community: Install LangChain's community edition to work with the LLM models.
(crewai_env) ranjan@aileaderx:/mnt/d/crewai$ pip install langchain_community
For detailed installation steps, please refer to the official CrewAI Installation Guide.
Code: CrewAI Blog Writer
This Python code initializes a multi-agent workflow using CrewAI and LangChain. Each agent (Researcher, Writer, Editor) is assigned a specific role in transforming factual data into an optimized blog post.
Complete Implementation
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
# Import necessary modules from CrewAI, LangChain, and utility libraries
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew # Core components for defining agents, tasks, and crew orchestration
from crewai_tools import ScrapeWebsiteTool # Tool for scraping content from a specified website
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAI # LangChain connector to interface with OpenAI-compatible models (like vLLM)
import warnings # Suppresses runtime warnings for a cleaner console output
# Disable all warning messages to avoid clutter in logs
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# -------------------------------------------
# 🔗 Step 1: Connect to Local LLM (vLLM Server)
# -------------------------------------------
# Use LangChain's ChatOpenAI interface to connect to a locally hosted DeepSeek-R1 model via OpenAI-compatible vLLM API
local_llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B", # Model name
base_url="http://localhost:8888/v1", # Local API endpoint (vLLM)
api_key="test-key", # Dummy key; vLLM does not enforce API keys
temperature=0.7 # Controls response creativity
)
# -------------------------------------------
# 🧠 Step 2: Define Agents with Specific Roles
# -------------------------------------------
# Agent 1: Researcher – Responsible for extracting facts and bullet-point insights
researcher = Agent(
role="Generative AI Analyst",
goal="Extract high-quality, accurate insights related to generative AI's role in 2025 software engineering",
backstory="An expert in AI research who can mine insights from trusted sources with precision.",
allow_delegation=False, # Prevent agent from handing off its task
verbose=True, # Enables agent to print its thought process
llm=local_llm # Connect this agent to the local LLM
)
# Agent 2: Writer – Converts insights into a well-structured article
writer = Agent(
role="Technical Blog Writer",
goal="Convert structured research into an engaging blog post about a given topic",
backstory="An experienced content creator who excels at turning research into readable blog articles.",
allow_delegation=False,
verbose=True,
llm=local_llm
)
# Agent 3: Editor – Enhances tone, clarity, and SEO
editor = Agent(
role="SEO Blog Editor",
goal="Edit blogs for clarity, tone, and SEO with strong meta tags and keyword optimization",
backstory="A skilled editor with a knack for making blogs rank higher on search engines.",
allow_delegation=False,
verbose=True,
llm=local_llm
)
# -------------------------------------------
# 🔧 Step 3: Define Tool(s)
# -------------------------------------------
# A simple web scraper tool that fetches content from Google’s AI blog
scraper = ScrapeWebsiteTool(
website_url="https://blog.google/technology/ai/"
)
# -------------------------------------------
# ✅ Step 4: Define Tasks with Inputs & Tools
# -------------------------------------------
# Task 1: Research – Researcher extracts bullet-point insights from web
research_task = Task(
description=(
"Research and extract factual insights about the topic: '{topic}'. "
"Use the provided website to gather accurate points about how generative AI is transforming software engineering in 2025. "
"Present the findings as bullet points, each with a source reference."
),
expected_output="A bullet-point factual summary with sources, directly related to the given topic.",
tools=[scraper], # Inject scraper tool into task
input_variables=["topic"], # Variables that will be replaced during execution
agent=researcher # Assign this task to the researcher agent
)
# Task 2: Writing – Writer creates the article draft from research
writing_task = Task(
description=(
"Based on the research findings about '{topic}', draft a full-length blog article. "
"Structure it with an engaging introduction, 3-4 meaningful sections, and a compelling conclusion. "
"Ensure the writing is coherent and relevant to 2025 trends in software engineering with generative AI."
),
expected_output="A structured, topic-aligned blog article with clear sections and compelling content.",
input_variables=["topic"],
agent=writer
)
# Task 3: Editing – Editor polishes the blog and optimizes for SEO
editing_task = Task(
description=(
"Polish the blog article related to '{topic}'. Optimize tone, clarity, and add SEO metadata. "
"Include a suitable title, meta-title, and meta-description. Ensure keyword alignment with terms like "
"'Generative AI', 'Software Engineering 2025', etc. Output final content only."
),
expected_output="Final version of the blog post, SEO-enhanced, with meta-title and meta-description.",
input_variables=["topic"],
agent=editor
)
# -------------------------------------------
# 🧩 Step 5: Crew – Orchestrate Agents and Tasks
# -------------------------------------------
crew = Crew(
agents=[researcher, writer, editor], # List of all participating agents
tasks=[research_task, writing_task, editing_task], # Ordered task pipeline
verbose=2, # Print crew-level debug info
memory=False # No long-term memory retention between runs
)
# -------------------------------------------
# 🚀 Step 6: Execute the Workflow
# -------------------------------------------
# Provide topic input that all tasks will use
inputs = {
"topic": "The impact of generative AI on software engineering in 2025"
}
# Run the workflow and print the final result
result = crew.kickoff(inputs=inputs)
print("\n🚀 Final Output:\n", result)
This example orchestrates a powerful, agent-driven workflow—all running locally with no cloud API dependency.
Crewai Blog Writer Console Logs
Below is Console Logs generated by the multi-agent CrewAI system.
Download Blog Writer Console Logs
Crewai Blog Writer Final Output (MD File format)
Below is the final blog content generated by the multi-agent CrewAI system. This includes research-backed content, structured blog formatting, and SEO-optimized metadata.
Download Blog Writer Final Output (MD File format)
Conclusion and Future Enhancements
This CrewAI-based blog writer demonstrates how autonomous agents can collaborate using clearly defined roles to generate high-quality content. By leveraging a local LLM setup via vLLM, it ensures privacy, performance, and cost-efficiency.
The integration of specialized agents—Researcher, Writer, and Editor—shows how LLMs can simulate human editorial workflows in an intelligent and structured manner.
The advantages of this architecture include:
- 🔗 Clear separation of responsibilities through dedicated agents
- ⚡ Local inference via DeepSeek-R1 and vLLM ensures privacy and speed
- 🧠 Reusability of logic for news summaries, whitepapers, or marketing copy
- 📈 Extensible to multi-agent workflows such as voice-over, distribution, or analytics
Potential Future Enhancements:
- 📚 Integration with local vector DBs for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- 🌍 Multilingual blog generation with translation and TTS agents
- 🧩 Plugin system to support custom research agents or editorial style guides
- 📊 Integration with analytics dashboards for blog performance tracking
Reference Links
- CrewAI Framework:
- vLLM Server:
- Model & LLM Tools: