Local Chatbot using Deepseek-R1 deployed using VLLM
vLLM Setup Guide for RTX 4060 (8GB VRAM) based Host
Optimized configuration for DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B and similar models
System Configuration
OS: Windows 11 WSL/Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
CPU: AMD Ryzen 9 HX (24 cores)
RAM: 32GB DDR5
GPU: NVIDIA RTX 4060 (8GB VRAM)
This guide works for both native Linux and Windows WSL environments. Choose models according to your hardware capabilities.
1. Installation & Setup
For Linux/WSL Environments
python3 -m venv vllm-env
source vllm-env/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install vllmPerformance Enhancements
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation # 18-25% speed boost
pip install transformers accelerate2. API Server Configuration
Recommended Parameters
| Parameter | Explanation | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|
| --model | Hugging Face model name or local path | deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B |
| --host | Network interface binding | 0.0.0.0 (all interfaces) |
| --port | API server port | 8888 |
| --device | Compute device | cuda (NVIDIA GPU) |
| --gpu-memory-utilization | VRAM allocation limit | 0.85 (85% of 8GB) |
| --max-model-len | Maximum context length | 32768 tokens |
| --max-num-seqs | Parallel request limit | 1 (single sequence) |
| --tensor-parallel-size | GPU parallelism | 1 (single GPU) |
| --swap-space | Host RAM fallback | 8 GB |
Start Command
python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8888 \
--device cuda \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.85 \
--max-model-len 32768 \
--max-num-seqs 1 \
--tensor-parallel-size 1 \
--swap-space 8- Increase --max-num-seqs for batch processing
- Reduce --gpu-memory-utilization for multi-application use
- Lower --max-model-len for faster responses
3. Model Selection Guide
Larger models (7B+) require quantization or better GPUs.
| Model Name | Size | VRAM Usage | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B | 1.5B | 5.2GB | General Purpose |
| TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat | 1.1B | 4.1GB | Fast Responses |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct | 7B | 7.8GB | Complex Tasks |
Local LLM Chatbot with DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B model loaded in vLLM
Private ChatGPT-style interface for locally hosted language models
Pre-Requisites
Required Python packages:
- streamlit:
pip install streamlit - openai:
pip install openai - vLLM:
pip install vllm
Additional requirements:
- vLLM server running locally on port 8888
- DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B model loaded in vLLM
System Architecture
Three-layer application structure:
- Streamlit UI: User interface and chat history management
- vLLM Client: OpenAI-compatible API wrapper
- Local LLM: DeepSeek model served through vLLM
Key Components Explained
1. ChatUI Class (chat_ui.py)
class ChatUI:
def __init__(self):
self._init_session()
def display_assistant_response(self, response):
# Typing effect implementation
for char in response:
display_text += char
bot_response.markdown(display_text + "▌")Manages chat interface, history, and typing animation.
2. VLLMChatClient (chat_client.py)
class VLLMChatClient:
def __init__(self, base_url, model_name):
self.client = OpenAI(base_url=base_url)
self.model = model_nameHandles communication with local vLLM server using OpenAI format.
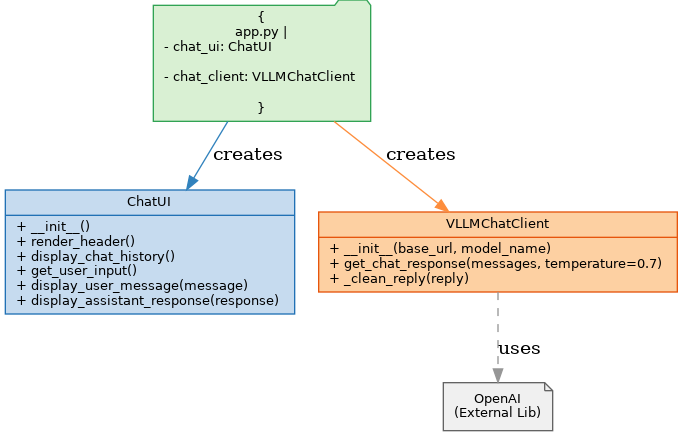
3. Main Application (app.py)
chat_ui = ChatUI()
chat_client = VLLMChatClient("http://localhost:8888/v1", "deepseek-model")
chat_ui.render_header()
chat_ui.display_chat_history()Orchestrates components and manages application flow.
User Interface Features
1. Chat Interface
prompt = chat_ui.get_user_input()
if prompt:
chat_ui.display_user_message(prompt)Real-time chat input with message persistence.
2. Typing Animation
for char in response:
display_text += char
bot_response.markdown(display_text + "▌")
time.sleep(0.01)Simulated typing effect for natural interaction.
3. Error Handling
try:
# Processing logic
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"❌ Error: {e}")Robust error handling for server communication issues.
Complete Implementation Files
chatbot-app/
├── app.py
├── chat_ui.py
├── chat_client.py
app.py
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
import streamlit as st
from chat_ui import ChatUI # Custom class for handling the Streamlit UI
from chat_client import VLLMChatClient # Custom class for interacting with the local vLLM server
# -----------------------------
# Step 1: Instantiate core components
# -----------------------------
# Create the ChatUI instance to manage user interface (title, input, chat display)
chat_ui = ChatUI()
# Create the VLLMChatClient instance to connect with the locally hosted LLM via vLLM server
chat_client = VLLMChatClient(
base_url="http://localhost:8888/v1", # URL where vLLM API is served
model_name="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B" # Name of the loaded LLM model
)
# -----------------------------
# Step 2: Render static UI components
# -----------------------------
# Display the chatbot title and description
chat_ui.render_header()
# Show all previous messages (chat history) stored in session state
chat_ui.display_chat_history()
# -----------------------------
# Step 3: Handle user input
# -----------------------------
# Show the chat input box and wait for user to type a message
prompt = chat_ui.get_user_input()
# -----------------------------
# Step 4: Process chat interaction
# -----------------------------
if prompt:
try:
# Display user's message in the chat window and save it to session state
chat_ui.display_user_message(prompt)
# Get model's reply from the local vLLM backend based on chat history
reply = chat_client.get_chat_response(st.session_state.messages)
# Show assistant's reply with typing effect and update chat history
chat_ui.display_assistant_response(reply)
except Exception as e:
# If something goes wrong (e.g., vLLM server isn't reachable), show error
st.error(f"❌ Error: {e}")
chat_client.py
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
from openai import OpenAI
class VLLMChatClient:
"""
A wrapper class to interact with a locally hosted vLLM server using the OpenAI-compatible API.
This handles sending the chat history and receiving responses from the LLM.
"""
def __init__(self, base_url: str, model_name: str):
"""
Initializes the client to connect with the local vLLM server.
Args:
base_url (str): The base URL where the vLLM server is running (e.g., "http://localhost:8888/v1").
model_name (str): The name of the locally loaded LLM model (e.g., "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B").
"""
# OpenAI-compatible client pointing to the local vLLM server.
# api_key is not required for local usage, but must be supplied.
self.client = OpenAI(base_url=base_url, api_key="not-needed")
self.model = model_name # Store the model name to be used for requests
def get_chat_response(self, messages, temperature=0.7):
"""
Sends the current conversation history to the model and retrieves a response.
Args:
messages (list): A list of message dictionaries (e.g., [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}]).
temperature (float): Controls randomness in output. Higher values = more creative responses.
Returns:
str: The assistant's reply after cleaning any hidden tags or system notes.
"""
# Send the chat messages to the model and get the completion
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model, # Use the specified local model
messages=messages, # Include the entire chat history
temperature=temperature # Set the creativity level
)
# Extract the assistant's reply text from the response
reply = response.choices[0].message.content
# Return a cleaned-up version of the reply
return self._clean_reply(reply)
def _clean_reply(self, reply: str) -> str:
"""
Cleans up the model's reply by removing any internal tags like or
that are sometimes present in system-level reasoning output.
Args:
reply (str): The raw response from the model.
Returns:
str: The cleaned response ready for display to the user.
"""
# If model includes hidden thoughts in ... format, remove them.
return reply.split("")[-1].strip()
chat_ui.py
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 AI Leader X (aileaderx.com). All Rights Reserved.
This software is the property of AI Leader X. Unauthorized copying, distribution,
or modification of this software, via any medium, is strictly prohibited without
prior written permission. For inquiries, visit https://aileaderx.com
"""
import streamlit as st
import time
class ChatUI:
"""
Handles the Streamlit-based user interface for the local LLM chatbot.
Manages UI rendering, user input, chat history display, and simulated typing effect.
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
Initializes the ChatUI instance and sets up session state for messages.
"""
self._init_session()
def _init_session(self):
"""
Ensures a session-level chat history is available.
If it doesn't exist, initializes an empty message list.
"""
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
def render_header(self):
"""
Displays the app's main title and an introductory markdown description.
This helps set the context for users interacting with the chatbot.
"""
st.title("🤖 Local AI Chatbot (vLLM + Streamlit)")
st.markdown("Chat with your locally running LLM powered by vLLM!")
def display_chat_history(self):
"""
Loops through the chat history stored in session state
and renders each message in the chat format based on the sender's role.
"""
for message in st.session_state.messages:
with st.chat_message(message["role"]): # "user" or "assistant"
st.markdown(message["content"]) # Render message content
def get_user_input(self):
"""
Displays a chat input field for the user to type their message.
Returns:
str: The text entered by the user (or None if nothing is typed).
"""
return st.chat_input("Type a message...")
def display_user_message(self, message):
"""
Renders the user's message in the chat and logs it to session history.
Args:
message (str): The user's input message.
"""
st.chat_message("user").markdown(message) # Show user message in chat bubble
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": message}) # Save it
def display_assistant_response(self, response):
"""
Renders the assistant's reply with a simulated "typing effect"
to enhance the user experience.
Args:
response (str): The text response generated by the model.
"""
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
bot_response = st.empty() # Placeholder for progressively updating text
display_text = ""
# Show the message one character at a time to mimic typing
for char in response:
display_text += char
bot_response.markdown(display_text + "▌") # Add blinking cursor
time.sleep(0.01)
bot_response.markdown(display_text) # Final message (remove cursor)
# Store the assistant's response in chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
Running the Application
Start the vLLM server:
vllm serve --model deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B
Example:
(vllm-env) aileaderx@LAPTOP-R6D2EB2M:/mnt/d$ python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server --model deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8888 --device cuda --gpu-memory-utilization 0.85 --max-model-len 32768 --max-num-seqs 1 --tensor-parallel-size 1 --swap-space 8
Launch the Streamlit interface:
chatbot-app$ streamlit run app.pyAccess the interface at:
- Local URL: http://localhost:8501
- Network URL: http://[your-ip]:8501
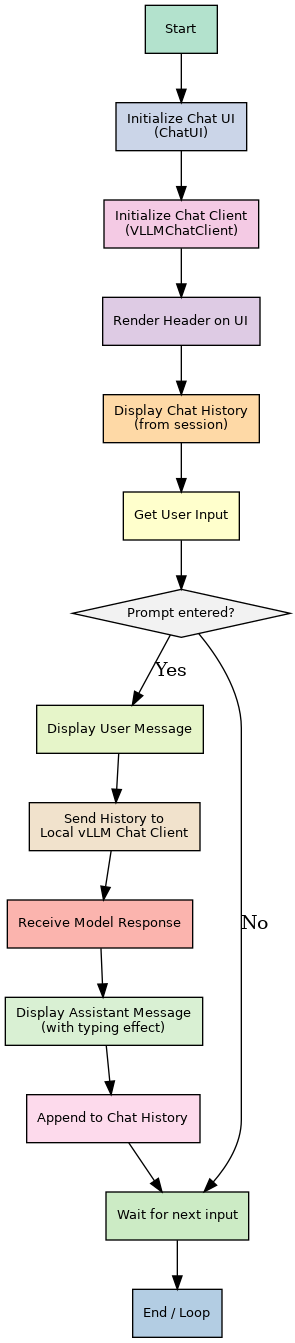
Sequence Flow of Chatbot using DeepSeek-R1 deployed via vLLM
Class Diagram of Chatbot using Deepseek-R1 deployed using VLLM
Chatbot using Deepseek-R1 deployed using VLLM - Output
Conclusion: Enterprise-Grade LLM Serving with vLLM
- ⚡ 3–5× Higher throughput than baseline LLM servers
- 📏 Supports up to 128K context tokens
- 🔄 Full OpenAI API compatibility
- 🔧 Optimized for real-time inference and low-latency streaming
- 📦 Supports Hugging Face models without conversion
- 🌐 Ideal for cloud-native or on-prem enterprise deployments
Core Capabilities
| Feature | Technical Benefit | Business Value |
|---|---|---|
| 🧠 PagedAttention | 55% memory reduction for long contexts | Process large documents efficiently |
| 🎭 Tensor Parallelism | Linear scaling across multiple GPUs | Deploy large models commercially |
| 📶 Token Streaming | 50ms first-token latency | Real-time interaction |
| 🧪 Speculative Decoding | Faster generation using draft models | Reduced inference time, lower cost |
| 📊 Multi-model Support | Serve multiple models concurrently | Improves deployment flexibility and availability |
| 📉 Memory Utilization Control | Fine-tune memory use via CLI | Optimal performance on limited GPUs |
vLLM vs Ollama Comparison
| Capability | vLLM | Ollama |
|---|---|---|
| Max Context Length | 128K Tokens | 4K–8K Tokens |
| Multi-GPU Support | ✅ Full support | ❌ Not available |
| Throughput | 250+ TPS | 50-80 TPS |
| Streaming Output | ✅ Token-by-token | ✅ Limited |
| Ease of Setup | Requires some configuration | Plug-and-play CLI |
| Enterprise Features | ✅ Observability, Auth, Scaling | ❌ Basic local only |
Implementation Guidelines
- 💡 Use Kubernetes for cloud-native scaling
- 💡 Implement JWT authentication for API security
- 💡 Monitor with Prometheus/Grafana
- 💡 Configure
--swap-spacefor large contexts - 💡 Utilize
--gpu-memory-utilizationto control memory usage - 💡 Use
--max-model-lenfor fine-tuning token limits
vLLM sets the standard for production LLM deployment, combining research-grade performance with enterprise reliability. While Ollama suits basic local use, vLLM excels in scalable, secure AI solutions. With capabilities like token streaming, multi-GPU inference, and memory-efficient paging, vLLM is ready for mission-critical AI infrastructure.
Reference Links & Resources
- vLLM Official Documentation: https://vllm.readthedocs.io/
- vLLM GitHub Repository: https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm
- Hugging Face Model Hub: https://huggingface.co/models
- Streamlit Documentation: https://docs.streamlit.io/
- OpenAI Python Client: https://github.com/openai/openai-python
- NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit
- DeepSeek Model Card: https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B